Wearable technology is revolutionizing construction site safety and productivity, emerging as one of the most significant construction safety innovations of the decade. Smart helmets, exoskeletons, and connected devices are transforming how construction professionals monitor worker health, prevent accidents, and optimize operational efficiency in real-time.
From biometric sensors that detect fatigue and heat stress to GPS-enabled wearables that establish geofenced safety zones, these advanced solutions provide unprecedented visibility into workplace safety metrics while enabling immediate response to potential hazards. Industry leaders implementing wearable technology report up to 27% reduction in workplace incidents and 20% improvement in project completion times.
As construction sites become increasingly complex and automated, wearable technology bridges the gap between human capability and project demands. These innovations not only enhance worker protection but also generate valuable data for risk assessment, compliance documentation, and operational optimization—making them an essential investment for forward-thinking construction companies focused on both safety and productivity.
Current Challenges in Construction Safety Management
The Human Factor: Limitations of Manual Safety Monitoring
Traditional safety monitoring in construction relies heavily on human supervision, which inherently presents several critical limitations. Safety managers and supervisors can only be present in one location at a time, making comprehensive site coverage challenging, especially on large-scale projects. Human fatigue and attention span constraints also impact the consistency and effectiveness of safety observations throughout long workdays.
Additionally, manual monitoring often suffers from delayed response times to potential hazards, as supervisors must physically travel between different areas of the construction site. The subjective nature of human observation can lead to varying interpretations of safety compliance and inconsistent enforcement of protocols across different shifts or teams.
Environmental factors such as poor visibility, extreme weather conditions, and high-noise environments further complicate manual safety monitoring efforts. These limitations, combined with the increasing complexity of modern construction projects and stricter safety regulations, highlight the need for more reliable and comprehensive monitoring solutions that can complement human supervision.
Cost of Construction Accidents and Injuries
Construction accidents and injuries pose significant financial burdens on companies, with industry data revealing staggering costs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, construction injuries result in direct costs exceeding $170 billion annually. The average workplace injury claim amounts to $41,000, while fatal accidents can exceed $1.2 million in total costs. These figures underscore the critical importance of effective construction risk management strategies.
Beyond direct medical expenses, companies face substantial indirect costs, including increased insurance premiums, lost productivity, worker replacement, legal expenses, and regulatory fines. OSHA estimates that indirect costs can be 4-10 times higher than direct costs. Project delays resulting from accidents typically extend timelines by 6-12 weeks, significantly impacting project budgets and client relationships. These financial implications have driven the construction industry’s growing interest in preventive safety measures, particularly wearable technology solutions that can help mitigate risks before incidents occur.
Advanced Wearable Safety Technologies in Action
Smart PPE and Connected Helmets
Smart PPE and connected helmets represent a significant advancement in construction safety technologies, offering unprecedented worker protection through real-time monitoring and data collection. These intelligent wearables incorporate sensors that detect environmental hazards, track vital signs, and monitor worker location with precision GPS capabilities.
Modern smart helmets feature integrated cameras, communication systems, and heads-up displays that provide workers with critical information without interrupting their tasks. Environmental sensors continuously monitor temperature, humidity, and the presence of harmful gases, while impact detection systems automatically alert supervisors in case of falls or collisions.
Recent implementations at major construction sites have demonstrated a 35% reduction in workplace incidents when using connected PPE systems. These devices transmit data to centralized safety monitoring platforms, enabling project managers to identify potential hazards before they escalate into accidents.
Key features of smart PPE include:
– Biometric monitoring for worker fatigue and heat stress
– Proximity warnings for heavy equipment
– Emergency SOS capabilities with precise location data
– Real-time communication channels between workers and supervisors
– Automatic documentation of safety compliance
The integration of these intelligent safety systems with project management platforms creates a comprehensive safety ecosystem that not only protects workers but also provides valuable data for improving site safety protocols and operational efficiency.
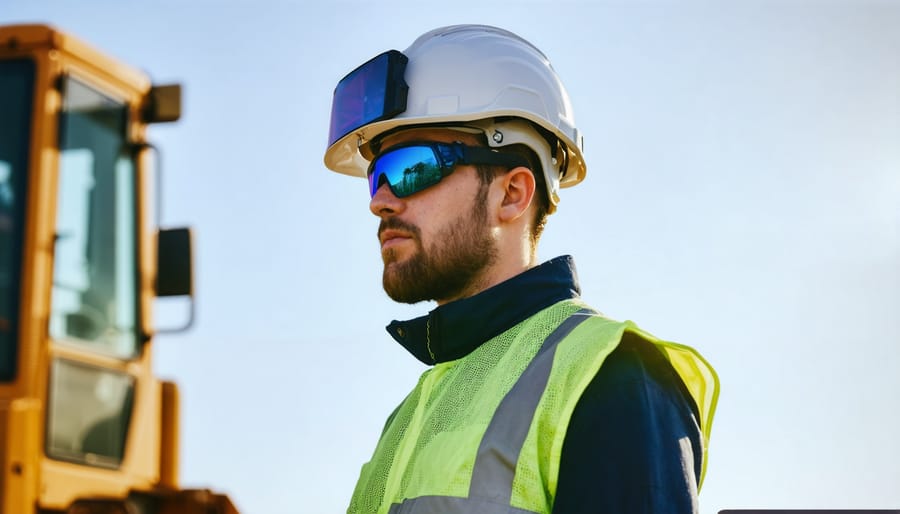

Biometric Monitoring Systems
Biometric monitoring systems represent a significant advancement in construction site safety, utilizing sophisticated sensors to track workers’ vital signs and fatigue levels in real-time. These wearable devices, often integrated into hard hats, safety vests, or wristbands, monitor key physiological indicators including heart rate, body temperature, movement patterns, and perspiration levels.
Advanced algorithms analyze this data to detect signs of fatigue, heat stress, or overexertion before they become critical issues. When predetermined thresholds are exceeded, these systems automatically alert both the worker and site supervisors, enabling immediate intervention. Some systems also track sleep patterns and overall physical strain, providing valuable insights into workforce wellness and potential safety risks.
Leading construction firms have reported significant improvements in accident prevention after implementing these monitoring solutions. For instance, a major infrastructure project in Singapore documented a 35% reduction in heat-related incidents after deploying biometric monitoring devices across their workforce.
Modern biometric systems also feature environmental sensors that correlate worker physiological data with ambient conditions such as temperature, humidity, and air quality. This comprehensive approach allows safety managers to make data-driven decisions about work schedules and rest periods, particularly during extreme weather conditions.
The collected data additionally supports long-term health management strategies, helping companies identify patterns and implement preventive measures to protect their workforce while optimizing productivity.
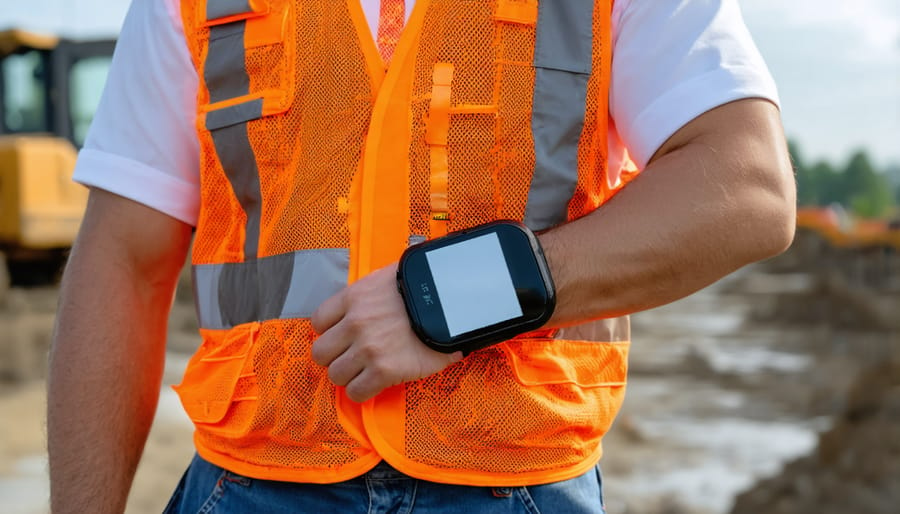

Environmental Hazard Detection Devices
Environmental hazard detection devices represent a crucial advancement in wearable construction technology, offering real-time monitoring of potentially dangerous workplace conditions. These sophisticated devices integrate seamlessly into standard personal protective equipment (PPE) and can detect various environmental threats, including toxic gases, excessive noise levels, and dangerous particulate matter.
Smart sensors embedded in hardhats and safety vests continuously monitor air quality, measuring levels of carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and other harmful gases commonly present at construction sites. These devices provide immediate alerts through vibration, audio signals, or smartphone notifications when detecting dangerous concentrations, allowing workers to evacuate hazardous areas promptly.
Advanced noise detection systems integrated into protective earmuffs measure decibel levels in real-time, helping prevent hearing damage and ensuring compliance with occupational safety standards. Similarly, dust and particulate matter sensors worn on workers’ lapels or integrated into face masks monitor exposure to silica dust and other harmful airborne particles.
Temperature and humidity sensors help prevent heat-related illnesses by alerting workers and supervisors when environmental conditions become dangerous. Some devices also incorporate UV exposure monitoring, particularly beneficial for outdoor construction projects.
These environmental monitoring devices often connect to central safety management systems, enabling safety officers to track exposure levels across the entire workforce and identify potential hazard patterns. This data-driven approach allows for proactive safety measures and helps maintain comprehensive safety records for regulatory compliance.
Implementation Success Stories
Major Construction Firm Case Study
Turner Construction, one of North America’s largest construction companies, implemented a comprehensive wearable technology program across 20 project sites in 2021, providing valuable insights into large-scale deployment effectiveness. The firm equipped 2,500 workers with smart hard hats featuring environmental sensors and location tracking capabilities.
The implementation process began with a three-month pilot program at two sites, followed by systematic rollout across remaining locations. Key features included real-time worker location tracking, fall detection, environmental monitoring, and proximity warnings for heavy equipment.
Initial results showed a 32% reduction in recordable incidents within the first six months. The technology proved particularly effective in preventing potential accidents, with 285 near-miss incidents logged and addressed proactively. Worker compliance reached 94% after initial resistance was addressed through comprehensive training and clear communication of benefits.
The financial analysis revealed an ROI of 287% over 18 months, with savings primarily from reduced insurance premiums, improved productivity, and accident prevention. Notable improvements included a 45% reduction in unauthorized zone entries and a 28% decrease in heat-related incidents.
Challenges encountered included initial connectivity issues in remote areas and battery life limitations, which were resolved through infrastructure upgrades and optimization of sensor activation protocols. The success of this implementation has led Turner to expand the program to all major projects, establishing wearable technology as a cornerstone of their safety protocol.
ROI and Safety Improvements
Recent industry studies demonstrate compelling ROI figures for wearable construction technology investments. Companies implementing these solutions report an average 27% reduction in workplace incidents and a 20% decrease in insurance premiums within the first year of deployment.
A comprehensive analysis of 150 construction sites revealed that firms using wearable safety devices experienced a 71% reduction in slip, trip, and fall incidents, while those utilizing smart PPE recorded a 35% decrease in repetitive strain injuries. The data shows that for every $1 invested in wearable technology, companies save approximately $4 in direct and indirect costs related to workplace accidents.
Real-time monitoring capabilities have proven particularly valuable, with emergency response times improving by an average of 72% on sites using connected worker solutions. Environmental sensors and biometric monitoring devices have helped prevent nearly 250 heat-related incidents across surveyed projects, representing a significant return on investment through avoided medical costs and productivity losses.
Financial benefits extend beyond safety improvements. Projects utilizing wearable technology report an average 12% increase in productivity through optimized workforce management and enhanced communication. Equipment-mounted sensors and worker-worn devices have reduced unauthorized equipment usage by 85%, leading to decreased maintenance costs and extended asset life cycles.
These quantifiable improvements make a strong business case for wearable technology adoption, particularly for large-scale construction operations where the potential for cost savings and risk reduction is substantial.
Integration and Implementation Strategies
Technology Selection and Deployment
Selecting and implementing wearable technology requires a strategic approach that goes beyond simply replacing traditional safety methods. Begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment of your construction operations, identifying specific safety challenges and operational inefficiencies that wearables could address.
Key selection criteria should include device durability, battery life, data accuracy, and compatibility with existing systems. Consider IP ratings for dust and water resistance, particularly for devices used in harsh construction environments. Evaluate the scalability of the solution and ensure it can integrate with your current safety management software and building information modeling (BIM) platforms.
Implementation should follow a phased approach, starting with a pilot program involving a small team of workers. This allows for testing the technology’s effectiveness and gathering user feedback before full-scale deployment. Provide comprehensive training sessions that address both technical operation and the benefits of adoption.
Create clear protocols for data collection, storage, and analysis. Establish metrics for measuring success, such as incident reduction rates and productivity improvements. Regular assessment of these metrics helps justify the investment and identify areas for optimization.
Remember to account for ongoing maintenance, updates, and support when budgeting for wearable technology. Partner with vendors who offer robust technical support and have experience in construction applications.
Worker Training and Compliance
Successful implementation of wearable construction technology requires a comprehensive training program and clear compliance protocols. Organizations should begin with a structured onboarding process that familiarizes workers with their specific wearable devices, including proper fitting, activation procedures, and basic troubleshooting.
Training sessions should be conducted in small groups to ensure hands-on experience and address individual concerns. These sessions must cover both technical operation and practical applications, emphasizing how the technology enhances workplace safety and productivity. Regular refresher courses keep workers updated on new features and reinforce best practices.
Compliance protocols should establish clear guidelines for daily use, maintenance responsibilities, and data handling procedures. Organizations must develop standard operating procedures (SOPs) that outline when and how devices should be worn, charging protocols, and steps for reporting malfunctions. These SOPs should align with existing safety policies and OSHA requirements.
To ensure sustained adoption, consider implementing a peer mentor system where experienced users support new adopters. Regular feedback sessions help identify challenges and opportunities for improvement. Performance metrics should track both usage rates and safety improvements, creating accountability while demonstrating value to stakeholders.
Documentation of training completion and compliance monitoring should be maintained in digital formats, enabling easy access for audits and regulatory requirements. Organizations should also establish clear consequences for non-compliance while recognizing and rewarding consistent proper usage.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, wearable safety technology stands at the forefront of transformative innovation, promising to revolutionize how we approach workplace safety and operational efficiency. The integration of smart PPE, biometric monitoring systems, and connected devices has already demonstrated significant improvements in accident prevention, worker wellness, and project productivity.
Looking ahead, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and advanced sensors will further enhance these wearable solutions, enabling predictive safety measures and more sophisticated real-time monitoring capabilities. The industry can expect to see increased adoption of mixed reality devices for training and operation, along with more sophisticated environmental monitoring systems integrated into standard safety equipment.
As costs decrease and technology becomes more accessible, even smaller construction firms will be able to implement these safety innovations. The future of construction safety lies in the seamless integration of wearable technology with existing safety protocols and management systems, creating a more connected, safer workplace environment. Companies that embrace these innovations now will be better positioned to meet future safety challenges while maintaining competitive advantage in an increasingly technology-driven industry.

