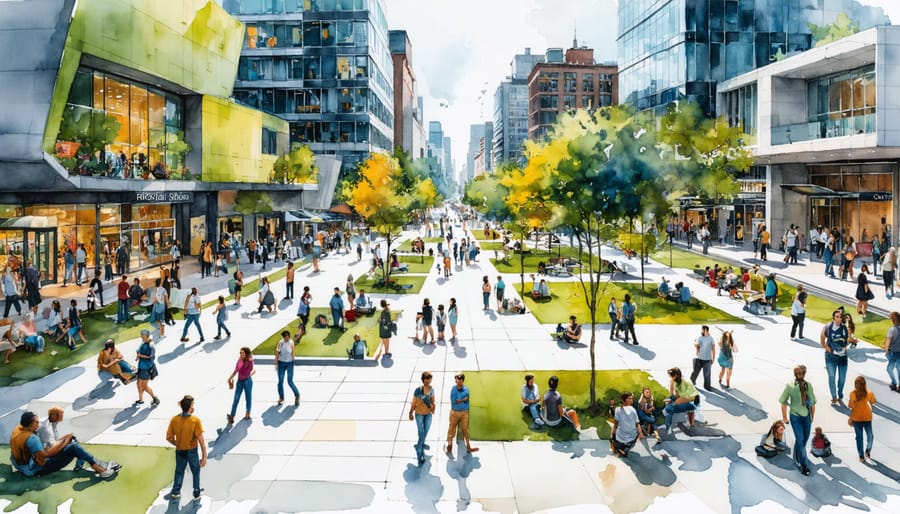
Human-centered design revolutionizes modern construction by placing end-user needs at the core of every architectural and engineering decision. This approach transforms traditional building practices into dynamic, user-focused solutions that enhance both functionality and human experience.
In today’s rapidly evolving construction landscape, successful projects demand more than technical excellence—they require a deep understanding of how people interact with built environments. Human-centered design bridges this gap by integrating behavioral insights, ergonomic principles, and user feedback throughout the development process, from initial concept to final implementation.
Leading construction firms and architects worldwide have documented up to 40% higher user satisfaction rates and 25% reduced post-occupancy modifications when implementing human-centered design methodologies. This systematic approach not only optimizes spatial efficiency and resource utilization but also creates environments that genuinely respond to human needs, behaviors, and aspirations.
By prioritizing user research, iterative testing, and continuous feedback loops, human-centered design ensures that construction projects deliver meaningful value beyond mere structural integrity. This introduction explores how this transformative approach reshapes our built environment while meeting the complex demands of modern society.
Core Principles of Human-Centered Urban Design
User Research and Community Engagement
Effective user research and community engagement form the cornerstone of successful human-centered design implementation. This process begins with systematic data collection through multiple channels, including structured interviews, focus groups, and observational studies of how people interact with existing spaces and structures.
Construction professionals should employ both qualitative and quantitative research methods to gather comprehensive community feedback. Surveys and questionnaires provide measurable data points, while ethnographic research offers deeper insights into user behaviors and preferences. Digital tools, such as online platforms and mobile applications, can facilitate continuous feedback collection throughout the project lifecycle.
Stakeholder workshops serve as crucial platforms for direct engagement, bringing together community members, design professionals, and project developers. These sessions should be carefully structured to encourage meaningful participation and ensure diverse perspectives are captured and incorporated into the design process.
Documentation and analysis of community input must be systematic and transparent. Feedback should be categorized, prioritized, and integrated into design decisions through a clear framework. Regular progress updates to stakeholders maintain engagement and trust, while iterative design reviews ensure community needs remain central to the project’s evolution.
The implementation phase should include mechanisms for ongoing feedback collection, allowing for adjustments based on real-world usage patterns and evolving community needs.
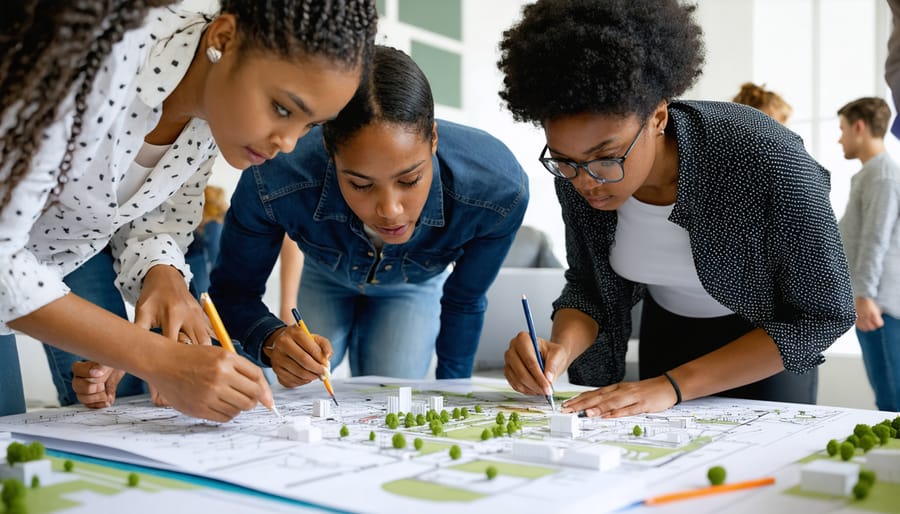

Inclusive Design Considerations
Inclusive design considerations form a crucial pillar of human-centered design, ensuring that built environments serve the entire community effectively. This approach requires careful attention to accessibility requirements, extending beyond basic compliance to create truly inclusive spaces. Key considerations include implementing universal design principles, such as level access routes, adequate lighting, and clear wayfinding systems that accommodate various physical and cognitive abilities.
Cultural sensitivity plays an equally important role in inclusive design. Projects must reflect and respect the diverse cultural backgrounds of end users, incorporating appropriate spatial arrangements, materials, and design elements that resonate with local communities. This might involve consulting with cultural groups during the planning phase and integrating traditional architectural elements where appropriate.
The diverse needs of different user groups must be carefully balanced. This includes considering the requirements of elderly residents, families with young children, people with disabilities, and individuals from various socioeconomic backgrounds. Successful inclusive design often incorporates flexible spaces that can adapt to different uses and user needs over time.
Regular stakeholder engagement and user feedback throughout the design process help ensure that inclusive design elements genuinely meet community needs rather than making assumptions about user requirements. This collaborative approach leads to more sustainable and socially responsible construction outcomes.
Collaborative Design Process Framework
Stakeholder Integration
Effective stakeholder integration is fundamental to successful human-centered design implementation in construction projects. This process requires systematic engagement with diverse groups, including end-users, project owners, contractors, regulatory bodies, and community representatives. By establishing clear communication channels and utilizing digital collaboration platforms, project teams can facilitate meaningful participation throughout the design lifecycle.
To ensure comprehensive stakeholder involvement, organizations should implement a structured engagement framework that includes:
1. Early identification and mapping of key stakeholders
2. Regular consultation workshops and feedback sessions
3. Documentation and incorporation of stakeholder inputs
4. Continuous validation of design decisions with affected parties
Successful integration requires careful balance between competing interests while maintaining focus on end-user needs. Project managers should establish clear protocols for conflict resolution and decision-making processes, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout stakeholder interactions.
Documentation plays a crucial role in stakeholder integration. Teams should maintain detailed records of engagement activities, decisions made, and resulting design modifications. This creates an audit trail that demonstrates due diligence and helps validate design choices during project reviews.
The key to effective stakeholder integration lies in maintaining consistent engagement throughout the project lifecycle, rather than limiting involvement to initial planning stages. This ongoing dialogue ensures that design solutions remain aligned with stakeholder needs while adapting to emerging requirements and constraints.
Design Iteration and Feedback Loops
Iterative design processes form the backbone of successful human-centered construction projects, establishing continuous improvement cycles that refine solutions based on user feedback and real-world performance data. The implementation of these feedback loops begins during the initial conceptual phase and extends throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that design decisions remain aligned with user needs and operational requirements.
Construction professionals can leverage innovative design visualization tools to facilitate meaningful stakeholder engagement and collect actionable feedback. These iterations typically follow a three-phase cycle: prototype development, user testing, and refinement based on collected data. Each cycle brings the design closer to optimal functionality while identifying potential issues before they become costly construction challenges.
Key components of effective feedback loops include:
– Structured user interviews and surveys
– Environmental behavior mapping
– Post-occupancy evaluations
– Real-time monitoring systems
– Regular stakeholder workshops
The success of iterative design processes depends on establishing clear metrics for evaluation and maintaining transparent communication channels with all stakeholders. Documentation of each iteration’s outcomes helps create a valuable knowledge base for future projects and supports data-driven decision-making throughout the construction process. This systematic approach to design refinement ensures that the final built environment truly serves its intended users while meeting technical and regulatory requirements.
Technology Integration in Human-Centered Design
The integration of technology in human-centered design has revolutionized how construction professionals approach project development and stakeholder engagement. Modern digital platforms have enhanced our ability to gather, analyze, and implement user feedback throughout the design process. Advanced collaborative architectural design tools now enable real-time visualization and modification of designs based on user input, significantly improving the iterative process.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) platforms have become instrumental in supporting human-centered design approaches by allowing teams to create detailed 3D representations that stakeholders can easily understand and interact with. These tools facilitate better communication between designers, clients, and end-users, ensuring that human needs remain at the forefront of decision-making.
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) technologies have transformed how we conduct user testing and spatial analysis. These immersive tools allow stakeholders to experience designed spaces before construction begins, providing valuable feedback that can be incorporated into the final design. This capability has proven particularly valuable in healthcare and educational facility projects, where user experience directly impacts operational efficiency.
Data analytics and artificial intelligence are increasingly being employed to process user feedback and behavior patterns, helping designers make more informed decisions. Smart sensors and IoT devices can track how people interact with existing spaces, providing quantitative data to support qualitative observations. This combination of technological capability and human insight creates a more robust foundation for design decisions.
Project management platforms specifically designed for human-centered approaches have emerged, incorporating features for stakeholder engagement tracking, feedback collection, and collaborative decision-making. These systems help maintain transparency throughout the design process and ensure that user needs remain central to project development.
Mobile applications for real-time feedback collection have also become essential tools, allowing designers to gather input from a broader range of users more efficiently. These apps often include features for photo documentation, voice recordings, and location-based feedback, making it easier to capture and analyze user experiences in context.
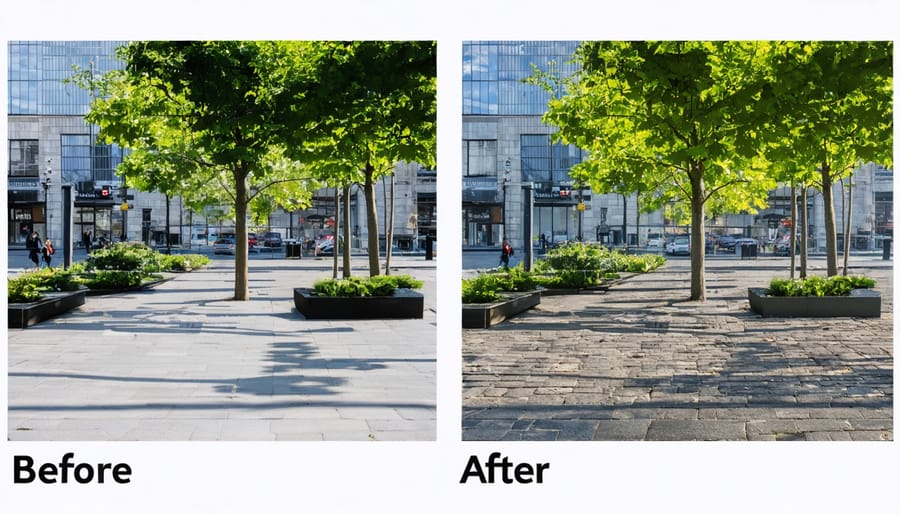

Case Study: Successful Urban Implementation
The transformation of Copenhagen’s Nørrebro district stands as a compelling example of human-centered design principles successfully applied to urban development. In 2018, the municipality embarked on a comprehensive neighborhood revitalization project that prioritized resident needs while addressing critical infrastructure challenges.
The project team, led by urban design firm Hansen & Partners, began with extensive community engagement, conducting over 200 interviews and organizing 15 community workshops over three months. This thorough discovery phase revealed that residents primarily sought improved pedestrian safety, more green spaces, and better social gathering areas while maintaining the district’s cultural identity.
Based on these insights, the design team developed solutions that directly addressed community needs. They implemented a “shared streets” concept, reducing vehicle speeds and creating wider sidewalks with integrated seating areas. The team also introduced pocket parks and urban gardens in previously underutilized spaces, increasing green coverage by 40%.
A notable innovation was the development of multi-functional public spaces that could adapt to different community needs throughout the day. For example, the central plaza features movable furniture and modular structures that transform from a morning market space to an evening entertainment venue, maximizing the utility of limited urban space.
The project’s success is evidenced by quantifiable metrics collected over the first two years post-completion:
– 65% increase in pedestrian traffic
– 45% reduction in traffic accidents
– 30% increase in local business revenue
– 85% resident satisfaction rate with new community spaces
The implementation team overcame several challenges, including initial resistance from local business owners concerned about reduced parking. Through transparent communication and demonstrable benefits to foot traffic, the team secured stakeholder buy-in. The project also incorporated innovative stormwater management systems within the new green spaces, addressing environmental concerns while creating aesthetic improvements.
This case study demonstrates how human-centered design principles, when properly applied, can create urban spaces that serve both functional and social needs while generating measurable positive outcomes for the community. The success in Nørrebro has since influenced similar projects across Northern Europe, establishing a benchmark for urban renewal initiatives.
Future Trends and Practical Applications
The future of human-centered design in construction is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing societal needs. Industry leaders are increasingly adopting collaborative design solutions that integrate artificial intelligence and real-time data analytics to better understand and respond to user behaviors and preferences.
Smart building technologies are emerging as a crucial trend, incorporating IoT sensors and adaptive systems that automatically adjust to occupant needs. These innovations allow buildings to respond dynamically to usage patterns, environmental conditions, and occupant feedback, creating more responsive and efficient spaces.
Virtual and augmented reality tools are revolutionizing the design validation process, enabling stakeholders to experience and evaluate spaces before construction begins. This technology significantly reduces the risk of design oversights and allows for more informed decision-making during the early stages of project development.
Practical implementation strategies for construction professionals include:
1. Early stakeholder engagement through digital platforms
2. Regular user feedback collection and analysis throughout the project lifecycle
3. Integration of behavioral data analytics in design decisions
4. Implementation of modular design elements for future adaptability
5. Incorporation of biometric monitoring systems for space optimization
The industry is also witnessing a shift toward sustainable human-centered design practices that prioritize both environmental impact and user well-being. This includes the use of biophilic design elements, natural lighting optimization, and materials that promote better indoor air quality.
Looking ahead, successful implementation will require construction professionals to develop new competencies in data analysis, user research methodologies, and digital technology integration. Organizations that invest in these capabilities now will be better positioned to deliver projects that truly meet user needs while maintaining operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
The successful implementation of human-centered design in construction projects requires a balanced approach that prioritizes user needs while maintaining technical excellence and project feasibility. Industry professionals should focus on early stakeholder engagement, comprehensive user research, and iterative design processes to achieve optimal outcomes. By incorporating behavioral insights, accessibility requirements, and sustainability considerations, projects can deliver lasting value for end-users while meeting business objectives. Moving forward, construction teams should establish clear metrics for measuring human-centered design success, invest in team training, and develop systematic approaches to user feedback integration. Remember that human-centered design is not just a phase but a continuous commitment throughout the project lifecycle, from initial concept to post-occupancy evaluation. This approach, when properly executed, leads to more successful projects, increased user satisfaction, and enhanced long-term value for all stakeholders.

