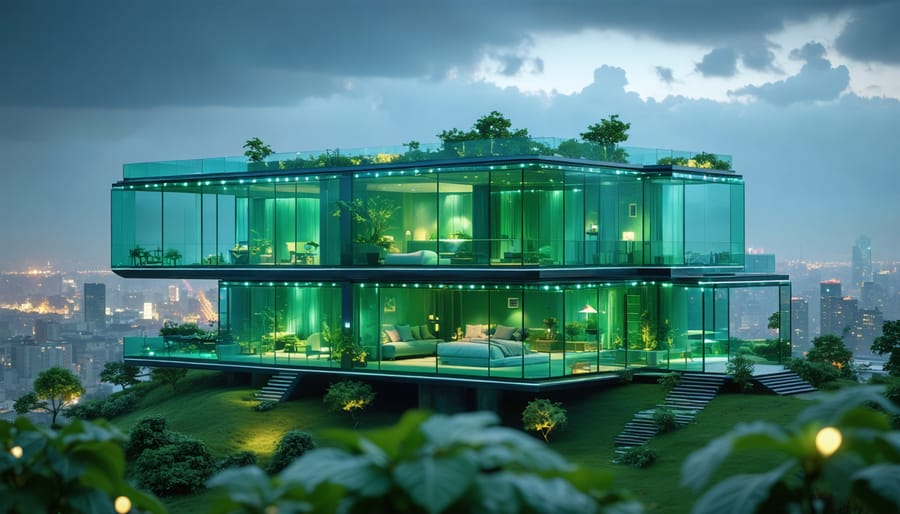
Glass modular homes represent a revolutionary convergence of architectural innovation and sustainable design, transforming the landscape of modern residential construction. Unlike traditional modular vs prefab construction, these sophisticated structures utilize advanced glazing systems and engineered structural frameworks to create transparent, energy-efficient living spaces that can be assembled with remarkable precision and speed. The integration of smart glass technology, thermal performance materials, and modular manufacturing processes has enabled construction professionals to deliver previously impossible combinations of aesthetic appeal and functional efficiency. Industry data reveals a 47% increase in glass modular home adoption over the past five years, driven by growing demand for sustainable, light-filled spaces and accelerated construction timelines. For builders and developers, these innovative structures represent not just an architectural statement, but a viable solution to meeting modern housing demands while maintaining strict quality control and reducing on-site construction complexity.
Revolutionary Design and Structural Innovation
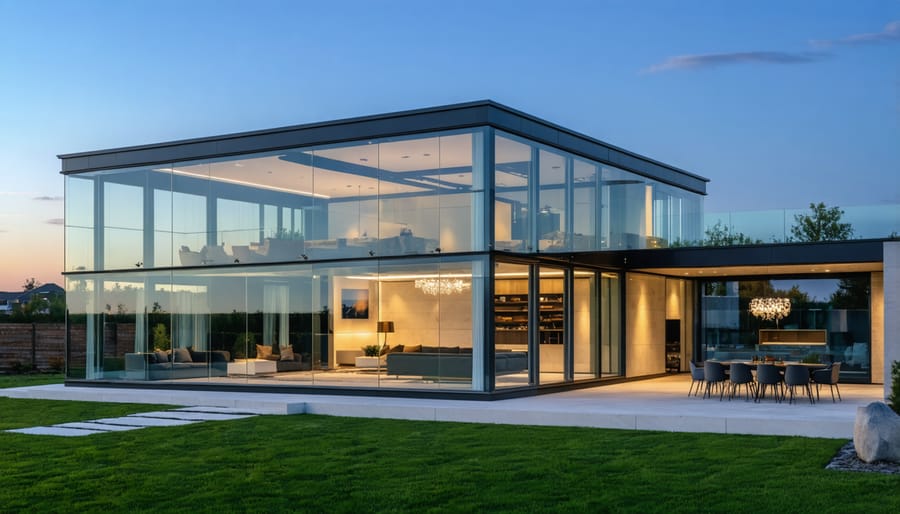

Advanced Glass Technologies
Modern glass modular homes leverage cutting-edge advanced building materials that significantly enhance their performance and functionality. Smart glass technology, including electrochromic and thermochromic variants, enables dynamic control over light transmission and solar heat gain. These systems can automatically adjust their opacity based on external conditions or user preferences, optimizing energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
The thermal performance of contemporary architectural glass has evolved dramatically, with triple-glazed units achieving U-values as low as 0.5 W/m²K. Low-E coatings and gas-filled cavities work in concert to minimize heat transfer while maintaining optimal visible light transmission. This advancement makes glass an increasingly viable option for modular construction in various climate zones.
Structural glass systems have also reached new heights in load-bearing capability. Laminated glass components, reinforced with interlayers like SentryGlas®, can now serve as primary structural elements. These systems demonstrate impressive strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced safety characteristics, meeting stringent building codes while enabling more ambitious architectural designs.
Integration of photovoltaic cells within glass panels further extends functionality, transforming building surfaces into energy-generating assets. Combined with smart home systems, these technologies create a sophisticated ecosystem that optimizes energy usage, security, and comfort levels throughout the structure.
Modular Framework Integration
Glass modular homes utilize an advanced integration system that seamlessly combines structural glass panels with traditional modular construction frameworks. The process involves precision-engineered connection points where tempered or laminated glass panels interface with steel or aluminum framing systems. These connection points typically feature specialized gaskets and thermal breaks to prevent thermal bridging and ensure optimal energy performance.
The integration framework employs a dual-purpose design approach, where glass panels serve both as architectural elements and structural components. Each panel connects to the primary modular frame through a series of engineered brackets and fastening systems, designed to accommodate thermal expansion and structural movement while maintaining weather-tight seals.
Critical to this integration is the implementation of unitized curtain wall principles adapted for modular construction. Factory-assembled glass units incorporate pre-installed mounting hardware, significantly reducing on-site installation time and ensuring quality control. The system typically includes integrated drainage channels, pressure-equalized rain screens, and vapor barriers within the frame assembly.
Modern glass modular systems feature smart joints that allow for dimensional tolerances and seismic considerations. These joints utilize EPDM gaskets or structural silicone sealants, creating flexible connections that maintain building envelope integrity while allowing for natural building movement. The integration system also incorporates specialized corner assemblies and transition details where glass modules interface with other building components, ensuring continuous thermal and moisture protection throughout the structure.
Environmental Performance and Energy Efficiency
Solar Gain Management
Solar gain management is crucial in glass modular homes, requiring sophisticated temperature control strategies to maintain optimal indoor comfort while maximizing energy efficiency. Advanced glazing technologies, including low-emissivity (low-e) coatings and spectrally selective glass, play a pivotal role in regulating heat transmission while preserving natural light penetration.
Modern glass modular homes typically incorporate dynamic shading solutions, such as electrochromic glass or automated external shading systems, which respond to changing environmental conditions. These systems can adjust their properties based on solar intensity, time of day, and seasonal variations, effectively managing heat gain during summer months while capitalizing on passive solar heating during winter.
Thermal break technology in framing systems creates an insulative barrier that minimizes heat transfer through the building envelope. When combined with double or triple-glazed units filled with inert gases like argon or krypton, these systems significantly enhance the structure’s thermal performance.
Integration of smart building management systems enables precise control over solar gain through automated adjustment of shading devices and HVAC systems. Real-time monitoring of internal temperatures and solar radiation levels ensures optimal thermal comfort while reducing energy consumption. Additionally, strategic orientation of glass panels and careful consideration of overhang designs during the planning phase can naturally regulate solar exposure throughout the year, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the modular structure.
Energy Conservation Systems
Glass modular homes incorporate sophisticated energy conservation systems that maximize efficiency while maintaining comfort and sustainability. These structures utilize advanced energy-efficient building solutions through integrated smart technologies and passive design principles.
The primary energy conservation features include double or triple-glazed glass panels with low-E coatings, which significantly reduce heat transfer while maintaining optimal natural light transmission. These specialized glass units typically achieve U-values between 0.8 and 1.2 W/m²K, substantially outperforming traditional building envelopes.
Smart climate control systems, incorporating AI-driven sensors and automated responses, optimize heating, cooling, and ventilation based on real-time environmental conditions. Building Management Systems (BMS) monitor and adjust energy consumption patterns, resulting in potential energy savings of 25-40% compared to conventional structures.
Solar heat gain is managed through electrochromic glass technology, which automatically adjusts tint levels based on sunlight intensity and interior temperature requirements. This dynamic response system eliminates the need for additional shading devices while maintaining optimal indoor conditions.
The integration of renewable energy systems, particularly building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), transforms glass surfaces into power-generating assets. Modern BIPV systems can achieve conversion efficiencies of up to 20%, contributing significantly to the building’s energy independence.
These conservation systems are complemented by smart grid integration capabilities, enabling demand-response participation and optimal energy storage management. The combination of these technologies typically results in annual energy consumption reductions of 50-70% compared to traditional construction methods, while maintaining superior comfort levels for occupants.
Construction and Installation Process
Factory Production
The production of glass modular homes takes place in controlled factory environments, where offsite manufacturing benefits ensure consistent quality and precision throughout the manufacturing process. Advanced automation systems and specialized equipment facilitate the precise cutting and assembly of glass panels, structural frames, and interior components.
Quality control measures are implemented at every stage of production, with thermal and structural testing conducted on glass components to verify their performance characteristics. Each module undergoes rigorous inspection protocols, including dimensional accuracy checks, weatherproofing assessments, and structural integrity evaluations. Computer-aided quality monitoring systems track production metrics in real-time, allowing immediate identification and correction of any deviations from specifications.
The factory setting enables strict environmental control, maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels for materials handling and assembly. This controlled environment eliminates weather-related delays and ensures proper curing of sealants and adhesives. Specialized jigs and fixtures guarantee precise alignment during assembly, while automated lifting systems facilitate safe material handling.
Before shipping, completed modules undergo final quality assurance testing, including pressure testing for air and water tightness, electrical systems verification, and finish inspection. This systematic approach to manufacturing results in consistently high-quality modules that meet or exceed building code requirements and industry standards.

On-Site Assembly
The on-site assembly of glass modular homes requires precise coordination and specialized equipment to ensure proper installation. Typically, the process begins with site preparation, including foundation work and utility connections, which must be completed before the modules arrive.
A standard installation timeline ranges from 2-5 days for basic configurations, though complex designs may require up to two weeks. The process employs crane-assisted placement, with each module carefully positioned according to predetermined alignment points. Critical to success is the use of protective handling equipment specifically designed for glass components.
Installation teams follow a systematic approach: first securing the base modules, then progressing upward level by level. Weather conditions significantly impact installation scheduling, with wind speeds under 20 mph and clear visibility being essential for safe module placement. Temperature fluctuations must also be considered, as they can affect glass expansion and contraction during installation.
Precision is paramount during the joining phase, where modules are connected using specialized gaskets and sealants designed for glass construction. Teams must ensure perfect alignment of all components to maintain structural integrity and thermal efficiency. Post-installation quality control includes comprehensive testing of all joints, seals, and mechanical systems.
The final phase involves connecting utilities, installing finishing elements, and conducting a thorough inspection to verify compliance with local building codes and manufacturer specifications. This methodical approach ensures the completed structure meets all safety and performance requirements.
Cost Analysis and Market Viability
Investment Considerations
The initial investment for a glass modular home typically ranges from $250-350 per square foot, positioning it in the premium segment of prefabricated construction. This cost encompasses structural components, specialized glazing systems, and factory assembly. Energy-efficient glass specifications and smart climate control systems represent approximately 30% of the total investment, while the structural framework accounts for 25%.
Long-term value assessment reveals significant advantages in operational costs. Studies indicate that modern glass modular homes achieve 40-50% reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional structures, primarily through advanced thermal insulation and solar heat management. Maintenance costs average 2-3% of the initial investment annually, primarily focusing on glazing system upkeep and mechanical components.
Property appreciation trends show glass modular homes maintaining value effectively, with annual appreciation rates of 4-6% in prime locations. Insurance premiums typically align with conventional construction rates, provided appropriate safety certifications are in place. Financing options have expanded, with several lenders offering specialized construction loans at competitive rates, reflecting growing market acceptance.
Return on investment calculations suggest a break-even period of 8-10 years when factoring in energy savings, reduced maintenance requirements, and property value appreciation. This timeline assumes proper implementation of energy-efficient systems and regular preventive maintenance protocols.
Market Growth Projections
Market analysis indicates that the glass modular home sector is poised for significant growth, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is driven by increasing demand for sustainable building solutions and innovative architectural designs in both residential and commercial sectors.
Industry experts forecast that the global market value for glass modular homes will reach $12.5 billion by 2025, with particularly strong growth in North America and Europe. The rise in urban population, coupled with the need for rapid construction solutions, is accelerating market penetration in metropolitan areas.
Environmental regulations and energy efficiency requirements are key factors influencing market growth. The integration of smart glass technologies and improved thermal performance characteristics is expected to drive adoption rates up by 25% over the next five years.
Investment in research and development within the sector has doubled since 2020, focusing on advanced manufacturing techniques and materials optimization. Market leaders are expanding production capabilities, with several major manufacturers announcing plans to increase capacity by 40% by 2024.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market, with China and Japan leading the adoption of glass modular construction technologies. This regional expansion is expected to contribute approximately 35% to global market growth by 2026.
Glass modular homes represent a transformative shift in contemporary construction, combining innovative design principles with sustainable building practices. As the construction industry continues to evolve, these structures are positioned to play a pivotal role in addressing modern housing challenges while meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards.
Industry projections indicate significant growth potential for glass modular construction over the next decade, driven by advancing technologies in smart glass, improved energy efficiency solutions, and streamlined manufacturing processes. The integration of automation and artificial intelligence in production facilities is expected to further reduce costs and increase precision, making glass modular homes more accessible to a broader market.
The future implications extend beyond residential applications. The principles and technologies developed for glass modular homes are increasingly influencing commercial construction, creating new possibilities for sustainable urban development. As cities worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, the adaptability and energy efficiency of glass modular construction position it as a viable solution for future building requirements.
However, success will depend on continued innovation in materials science, installation methodologies, and regulatory frameworks. Industry leaders must work closely with policymakers and environmental experts to establish standards that ensure these structures meet both performance and sustainability goals. With proper development and implementation, glass modular homes could fundamentally reshape our approach to residential construction, offering a blueprint for environmentally conscious, efficiently manufactured housing solutions.

