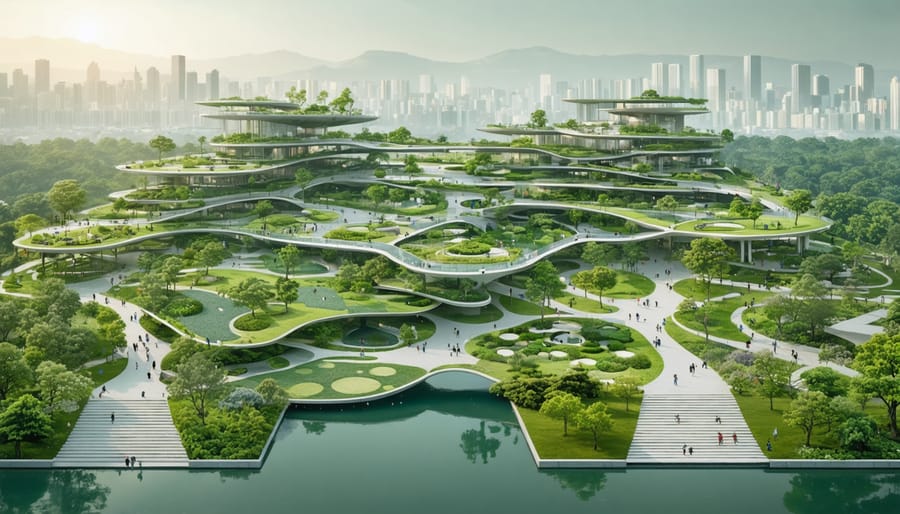
Landscape architecture transcends mere aesthetic appeal, emerging as a critical intersection of environmental science, urban planning, and sustainable design. Modern landscape architects orchestrate complex systems that balance human needs with ecological preservation, creating spaces that serve both form and function. Through innovative integration of natural elements, technological advancement, and architectural principles, today’s landscape design reshapes our built environment to address climate resilience, biodiversity conservation, and social connectivity.
The discipline has evolved from traditional garden design into a sophisticated field that influences urban development, environmental preservation, and public health. Contemporary landscape architects leverage advanced modeling software, sustainable materials, and biophilic design principles to create environments that reduce urban heat islands, manage stormwater systems, and foster community engagement. Their work extends beyond aesthetic considerations to encompass critical infrastructure planning, ecosystem services, and climate adaptation strategies.
As cities expand and environmental challenges intensify, landscape architecture stands at the forefront of developing solutions for sustainable urban development. The field combines rigorous technical expertise with creative vision, employing evidence-based design methodologies to create resilient, adaptable spaces that serve multiple functions while maintaining ecological integrity. This strategic approach to landscape design has become essential in addressing contemporary challenges such as climate change, urbanization, and the increasing need for sustainable development practices.
The Integration of Built and Natural Environments

Sustainable Design Principles
Sustainable landscape design has evolved significantly in recent years, integrating energy-efficient design principles with ecological preservation strategies. Modern landscape architects prioritize water conservation through innovative irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting, and drought-resistant plant selection. These approaches not only reduce maintenance costs but also ensure long-term environmental sustainability.
The implementation of bioswales and rain gardens has become instrumental in managing stormwater runoff, while permeable paving systems allow natural groundwater recharge. Native plant species selection plays a crucial role, supporting local biodiversity and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and excessive irrigation.
Materials selection has also transformed, with emphasis on recycled and locally-sourced materials that minimize transportation emissions and support regional economies. Green walls and roofs are increasingly integrated into designs, providing thermal insulation, reducing urban heat island effects, and creating habitats for local wildlife.
Smart technology integration enables precise resource management through automated irrigation systems and real-time monitoring of soil conditions. These systems optimize water usage and maintain plant health while reducing operational costs. Landscape architects now routinely incorporate renewable energy features, such as solar-powered lighting and water features, further reducing environmental impact.
The success of sustainable landscape design relies on thorough site analysis, understanding local climate patterns, and careful consideration of maintenance requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
Climate-Responsive Design
In modern landscape architecture, climate-responsive design has become a cornerstone of sustainable development. Practitioners must carefully analyze local climate patterns, including temperature variations, precipitation levels, wind patterns, and solar exposure to create resilient outdoor spaces. This approach integrates climate-responsive building materials and strategic design elements to optimize environmental performance.
Key considerations include water management through permeable surfaces and bioswales, strategic placement of vegetation for natural cooling and wind protection, and the selection of native plant species adapted to local conditions. Landscape architects employ sophisticated modeling tools to predict seasonal changes and design accordingly, incorporating features like shade structures, water features, and thermal mass elements to moderate temperature extremes.
Successful climate-responsive designs often utilize microclimatic manipulation techniques. These include creating wind breaks with strategic plant placement, managing solar gain through careful hardscape positioning, and establishing moisture-retention zones. The integration of smart irrigation systems and drought-resistant landscaping helps maintain sustainability during periods of water scarcity.
Professional landscape architects must also account for climate change projections, designing spaces that can adapt to evolving environmental conditions. This forward-thinking approach ensures long-term project viability while minimizing maintenance requirements and environmental impact. The result is a landscape that not only survives but thrives within its specific climatic context.
Technical Elements of Modern Landscape Design
Site Analysis and Planning
Site analysis and planning form the critical foundation of successful landscape architecture projects, requiring a systematic approach to data collection and evaluation. The process begins with comprehensive site surveys that document existing conditions, including topography, soil composition, drainage patterns, and vegetation. Modern professionals utilize advanced tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and drone mapping technology to create detailed site analyses with unprecedented accuracy.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the evaluation process. Professionals must assess microclimatic conditions, including sun patterns, prevailing winds, and seasonal changes. This data influences decisions about plant selection, hardscape materials, and spatial organization. Additionally, careful consideration of existing ecosystems and wildlife corridors ensures that new designs integrate seamlessly with natural systems.
Master planning involves synthesizing site analysis data with client requirements and regulatory constraints. This phase typically includes creating bubble diagrams and conceptual layouts that establish spatial relationships and circulation patterns. Professional landscape architects employ 3D modeling software to visualize different scenarios and test design solutions before implementation.
Sustainable site planning has become increasingly important, with emphasis on stormwater management, habitat preservation, and energy efficiency. Tools like the Sustainable SITES Initiative provide frameworks for evaluating and improving site sustainability. Furthermore, careful consideration of maintenance requirements during the planning phase ensures long-term project success and reduces operational costs.
Material Selection and Implementation
In contemporary landscape design, effective material selection strategies play a pivotal role in creating sustainable, aesthetically pleasing, and functionally superior outdoor spaces. Modern landscape architects increasingly favor materials that balance durability with environmental responsibility, incorporating both traditional and innovative options.
Natural stone remains a cornerstone material, with granite and limestone leading preferences for hardscaping elements due to their resilience and timeless appeal. However, engineered composites and recycled materials are gaining prominence, offering enhanced performance characteristics while reducing environmental impact. Permeable pavers and sustainable concrete alternatives demonstrate this evolution, providing superior water management capabilities while maintaining structural integrity.
For vertical elements and structures, weather-resistant woods like cedar and ipe continue to be popular, though modified wood products and high-performance composites are emerging as viable alternatives. These materials offer extended lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements while maintaining the organic aesthetic that clients often desire.
Innovative materials such as photocatalytic concrete, which helps reduce air pollution, and self-healing surfaces that minimize maintenance costs, represent the cutting edge of landscape material technology. When implementing these materials, consideration must be given to local climate conditions, usage patterns, and long-term maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Water Management Systems
Modern water management systems in landscape design integrate sophisticated drainage solutions, sustainable irrigation technologies, and water conservation strategies to maximize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. These systems typically incorporate smart controllers that adjust water distribution based on real-time weather data and soil moisture levels, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Advanced drainage solutions now include bioswales, rain gardens, and permeable pavements that naturally filter stormwater while reducing runoff. These features work in conjunction with underground detention systems and engineered soils to manage water flow effectively during peak rainfall events.
Irrigation technology has evolved to include precision drip systems, rotating sprinkler nozzles, and subsurface irrigation networks that deliver water directly to plant root zones. These systems can be programmed to operate during optimal times, reducing evaporation losses and improving water use efficiency by up to 30-50% compared to traditional methods.
Water conservation strategies often incorporate rainwater harvesting systems, greywater recycling, and drought-resistant plant selection. Smart meters and leak detection systems provide real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing immediate response to system failures or inefficiencies.
For maximum effectiveness, these components should be integrated into a comprehensive water management plan that considers local climate conditions, soil characteristics, and specific site requirements. Regular maintenance and system audits ensure continued efficiency and compliance with local water management regulations.
Digital Innovation in Landscape Architecture
3D Modeling and Visualization
Modern landscape design has been revolutionized by advanced 3D modeling and visualization tools, which have become integral to the design development process. Industry-standard software like AutoCAD Civil 3D, SketchUp, and Lumion enable designers to create highly detailed, photorealistic representations of landscape projects before breaking ground.
These tools facilitate precise terrain modeling, vegetation placement, and hardscape integration while allowing real-time visualization of seasonal changes, lighting conditions, and shadow patterns. Professionals can now generate accurate topographical models, calculate cut-and-fill volumes, and analyze drainage patterns with unprecedented accuracy.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) integration has further enhanced the capability to coordinate landscape elements with architectural and engineering components. This integration enables clash detection, improved cost estimation, and more effective project planning. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications have added another dimension to client presentations, allowing stakeholders to experience designed spaces through immersive walkthroughs.
The adoption of these technologies has significantly reduced design iterations, minimized construction errors, and improved communication between project stakeholders. Real-time rendering capabilities enable immediate visualization of design modifications, facilitating more informed decision-making during client meetings and regulatory reviews. This technological evolution has not only streamlined the design process but has also elevated the standard of landscape architecture presentation and implementation.

Smart Landscape Solutions
The integration of smart technology in landscape design represents a transformative shift in how we approach outdoor spaces. By leveraging innovative construction technologies, landscape architects can now create environments that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly efficient and sustainable.
Smart irrigation systems equipped with weather sensors and soil moisture monitors optimize water usage by automatically adjusting watering schedules based on real-time environmental conditions. These systems can reduce water consumption by up to 50% while maintaining optimal plant health. Integration with building management systems (BMS) allows for seamless coordination between indoor and outdoor environments.
LED lighting systems with motion sensors and programmable controls enhance security while reducing energy consumption. Smart materials, such as permeable pavements with embedded sensors, can monitor water quality and manage stormwater runoff more effectively. Climate-responsive shade structures automatically adjust their position based on sun tracking algorithms, maximizing comfort in outdoor spaces.
Remote monitoring capabilities enable landscape managers to track system performance, detect issues before they become critical, and implement preventive maintenance schedules. Mobile applications provide real-time data on landscape health, water usage, and energy consumption, allowing for data-driven decision-making in landscape management.
These smart solutions not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to LEED certification goals and sustainable development objectives, making them increasingly essential in modern landscape architecture projects.
Case Studies in Excellence
Urban Park Transformations
Recent urban landscape transformations have demonstrated the profound impact of thoughtful design on city environments. Notable examples include New York’s High Line, which reimagined an abandoned railway line into a 1.45-mile elevated park, serving as a blueprint for adaptive reuse in urban settings. The project’s success lies in its innovative integration of native plantings, preserved rail elements, and carefully planned gathering spaces that support both social interaction and ecological diversity.
In Toronto, the revitalization of Waterfront Park showcases how landscape architects can address climate resilience while creating vibrant public spaces. The park incorporates bioswales, permeable surfaces, and strategic tree placement to manage stormwater runoff, while flexible event spaces and recreational areas serve diverse community needs. The project’s sophisticated drainage systems and native plant selection demonstrate how technical expertise can align with aesthetic excellence.
Seoul’s Cheonggyecheon Stream restoration project exemplifies large-scale urban transformation. This former elevated highway was converted into a 3.6-mile linear park, featuring a restored stream, pedestrian walkways, and cultural spaces. The project significantly reduced urban heat island effects and improved air quality while creating a popular public amenity that attracts millions of visitors annually.
These transformations share common success factors: comprehensive stakeholder engagement, attention to environmental sustainability, and integration of smart technology for maintenance and monitoring. Successful urban park projects typically incorporate:
– Flexible programming spaces that accommodate multiple uses
– Sustainable materials and construction methods
– Indigenous vegetation suited to local climate conditions
– Smart irrigation systems and water management solutions
– Universal accessibility features
– Integration with existing urban infrastructure
The measurable benefits of these transformations extend beyond aesthetics, including increased property values, improved public health outcomes, and enhanced environmental resilience. Modern urban park design increasingly emphasizes the creation of multifunctional spaces that serve both ecological and social purposes, setting new standards for landscape architecture in dense urban environments.
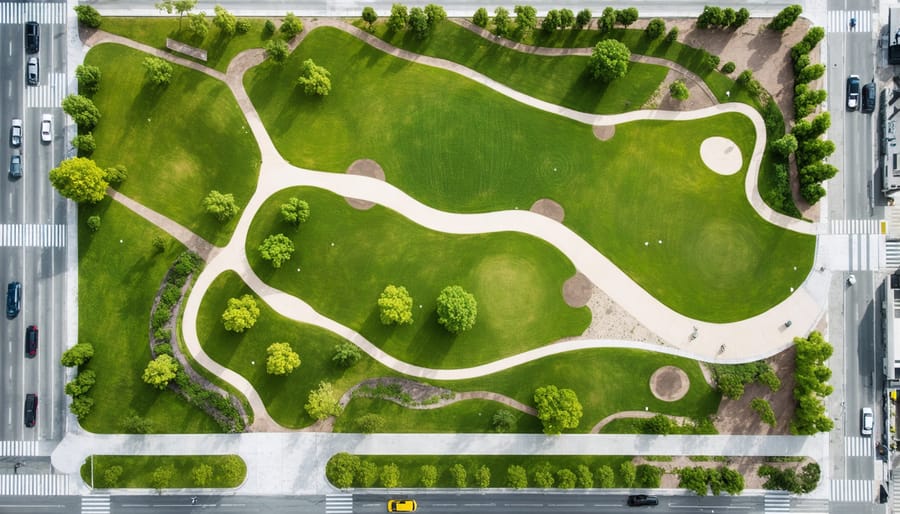

Commercial Development Integration
Commercial landscape architecture plays a pivotal role in shaping successful business environments, merging aesthetic appeal with functional design to create spaces that attract customers and enhance property value. The integration process begins during the initial planning phase, where landscape architects collaborate with commercial developers to establish a cohesive vision that aligns with the project’s goals and budget constraints.
Key considerations in commercial landscape design include traffic flow patterns, accessibility requirements, and sustainable design practices. Architects must carefully balance hardscape elements like walkways, parking areas, and gathering spaces with strategic plant selection and placement. This integration requires detailed understanding of local zoning regulations, environmental factors, and maintenance requirements.
Modern commercial developments increasingly emphasize sustainable landscape solutions, incorporating features such as bioswales, rain gardens, and native plant species. These elements not only reduce environmental impact but also minimize long-term maintenance costs while creating visually appealing spaces that resonate with environmentally conscious consumers.
The success of commercial landscape integration often depends on careful consideration of sight lines, entry points, and brand identity expression through design elements. For retail developments, creating inviting storefronts and comfortable pedestrian zones can significantly impact foot traffic and customer retention. Office complexes benefit from thoughtfully designed outdoor workspaces and recreational areas that promote employee well-being and productivity.
Water management stands as a critical component, with sophisticated irrigation systems and drainage solutions integrated seamlessly into the overall design. Smart technology implementation allows for efficient resource management while maintaining optimal landscape health throughout the seasons.
Recent trends show increased demand for mixed-use development landscapes that create seamless transitions between retail, office, and residential spaces. These integrated designs often incorporate multi-functional areas that serve various purposes throughout the day, maximizing space utility while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
The most successful commercial landscape projects demonstrate a careful balance between immediate visual impact and long-term sustainability, ensuring that the investment continues to provide value throughout the property’s lifecycle.
The landscape architecture industry stands at a pivotal point of transformation, driven by sustainability imperatives, technological advancement, and evolving urban needs. Current trends indicate a strong shift toward climate-resilient design solutions, with professionals increasingly incorporating native plantings, water-efficient systems, and biodiversity-supporting features into their projects.
Digital technologies continue to reshape the field, with Building Information Modeling (BIM), virtual reality, and advanced visualization tools becoming standard practice. These innovations enable more precise planning, better stakeholder communication, and more efficient project execution. The integration of smart technology in landscape design is also gaining momentum, from automated irrigation systems to sensor-based maintenance solutions.
Looking ahead, the industry is poised for significant evolution. Climate change adaptation will likely become a central focus, with growing emphasis on green infrastructure, urban heat island mitigation, and stormwater management. The concept of biophilic design is expected to expand beyond individual projects to influence entire urban planning strategies.
Emerging trends suggest increased demand for multifunctional spaces that serve both environmental and social purposes. Projects will likely emphasize community engagement, health and wellness, and ecological restoration while maintaining aesthetic appeal. The rise of vertical gardens, rooftop landscapes, and urban agriculture indicates a future where landscape architecture plays a crucial role in maximizing limited urban space.
The profession’s future outlook remains strong, with growing recognition of landscape architects’ role in addressing climate change, urbanization, and public health challenges. Success in the field will require continuous adaptation to new technologies, sustainable practices, and evolving client needs while maintaining core design principles and environmental stewardship.

