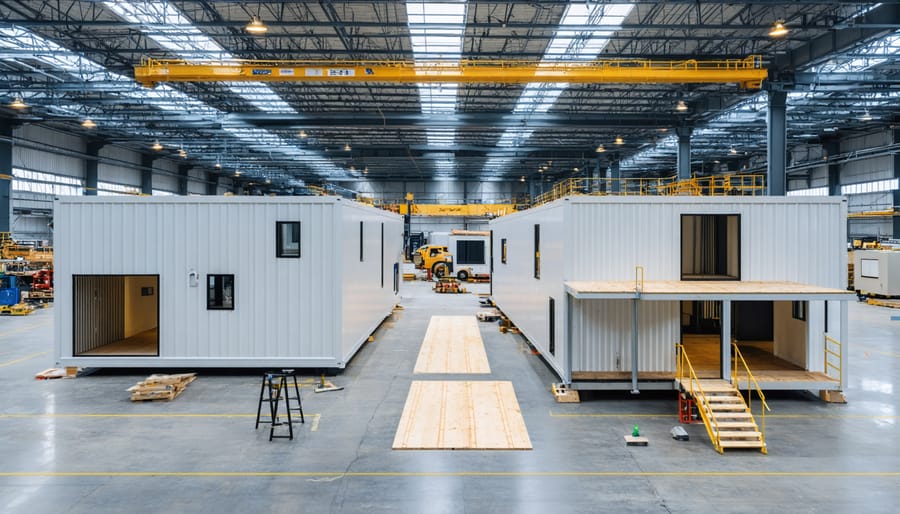
The evolving landscape of modern construction presents two distinct yet often misunderstood approaches: modular and prefabricated homes. While both methods revolutionize traditional construction through off-site manufacturing, their fundamental differences significantly impact project outcomes, costs, and timeline expectations. Modular homes emerge from complete box-like units manufactured in controlled factory environments, whereas prefab construction encompasses a broader spectrum of pre-manufactured components assembled on-site. This distinction proves crucial for construction professionals navigating today’s demanding market requirements for efficiency, quality control, and sustainable building practices.
As project complexity and labor costs continue to rise, understanding these methodologies becomes essential for architects, developers, and construction managers seeking to optimize their building strategies. The choice between modular and prefab construction affects everything from initial design considerations to final inspection protocols, making it a critical decision point in the early stages of project planning. This comprehensive analysis explores the technical specifications, regulatory frameworks, and practical implications that distinguish these two innovative construction approaches, enabling industry professionals to make informed decisions aligned with their project objectives.
Manufacturing Process and Construction Methods
Modular Home Construction
Modular home construction represents a sophisticated evolution in the offsite manufacturing process, where individual modules or sections are fabricated under controlled factory conditions. These three-dimensional units are engineered to precise specifications, typically comprising complete rooms or housing sections that include electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems pre-installed.
Each module undergoes rigorous quality control inspections throughout production, adhering to specific building codes and structural requirements. The units are constructed using steel frames or engineered wood systems, designed to withstand transportation stresses and maintain structural integrity during assembly. Standard modules typically measure 12-16 feet in width and up to 60 feet in length, though dimensions can vary based on project specifications.
The factory environment enables consistent production quality, weather-independent construction, and significant waste reduction compared to traditional building methods. Once manufactured, these modules are transported to the construction site, where cranes lift and position them onto prepared foundations. Specialized crews then complete the final connections, including utility hookups, exterior finishing, and weatherproofing.
This systematic approach typically reduces construction time by 30-50% compared to conventional methods, while maintaining superior quality control and structural integrity. The process requires careful coordination between factory production schedules, transportation logistics, and on-site assembly teams to ensure efficient project completion.

Prefab Home Assembly
Prefabricated home assembly involves a systematic approach where factory-manufactured components are transported to the construction site for final assembly. These components typically include wall panels, roof trusses, floor systems, and pre-fitted utility cores. The assembly process begins with site preparation and foundation work, which must be completed to precise specifications to ensure proper alignment with the prefabricated elements.
A critical phase involves the careful coordination of component delivery and installation sequences. Heavy machinery, including cranes and specialized lifting equipment, positions the major structural elements. Skilled crews then connect these components using predetermined joining methods, such as mechanical fasteners, welding, or specialized coupling systems.
The exterior envelope assembly includes the installation of pre-manufactured wall panels, which often come complete with integrated insulation, vapor barriers, and exterior finishing. Roof systems are typically assembled from pre-engineered trusses and panels, designed for rapid installation while maintaining structural integrity.
Interior finishing follows a predetermined sequence, with pre-fitted mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems requiring precise connection points. Quality control inspections occur at multiple stages throughout the assembly process, ensuring compliance with building codes and manufacturer specifications. Weather protection measures are essential during assembly, as exposure to elements can affect component integrity and installation quality.
The entire assembly process typically requires 30-60% less time compared to traditional construction methods, though this varies based on project complexity and site conditions.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Modular Design Capabilities
Modern modular homes offer unprecedented design flexibility, diverging significantly from traditional perceptions of cookie-cutter prefabricated structures. Today’s modern modular construction solutions accommodate diverse architectural styles, from contemporary minimalist designs to traditional aesthetics.
These structures can be engineered to include sophisticated features such as vaulted ceilings, multiple stories, and complex roof configurations. The modular format allows for customization within standardized parameters, enabling architects to create unique designs while maintaining manufacturing efficiency. Typical modules range from 12 to 16 feet in width and up to 60 feet in length, offering substantial flexibility in floor plan configurations.
Design constraints primarily revolve around transportation logistics and structural requirements. Modules must maintain structural integrity during transport and installation, necessitating specific engineering considerations. However, these limitations have driven innovation in connection systems and assembly methods, resulting in increasingly sophisticated design possibilities.
Advanced CAD systems and BIM technology enable precise design coordination between architects, manufacturers, and contractors, ensuring seamless integration of modules while maintaining design integrity. This technological integration has significantly expanded the architectural possibilities within the modular construction framework.
Prefab Design Possibilities
Prefab homes offer remarkable design flexibility, ranging from minimalist contemporary structures to elaborate custom estates. Unlike common misconceptions, prefabricated construction doesn’t limit architectural creativity; instead, it provides a structured framework for innovative design implementation. Modern prefab manufacturers utilize advanced CAD systems and BIM technology to create highly customized solutions while maintaining the efficiency of factory production.
Design possibilities include single-story ranches, multi-level contemporaries, and even complex architectural statements featuring curved walls and expansive glass facades. Manufacturers typically offer base models that can be modified with various exterior finishes, roof styles, and floor plan configurations. Some companies provide completely custom design services, working with architects to translate unique visions into prefabricated components.
Material options are equally diverse, encompassing traditional wood framing, steel construction, SIPs (Structural Insulated Panels), and hybrid systems. Exterior finishing choices range from conventional siding and brick to modern metal panels and sustainable materials. Interior specifications can include high-end finishes, smart home integration, and energy-efficient systems.
The key to successful prefab design lies in early planning and understanding manufacturing constraints while maximizing available customization options. This approach ensures both design integrity and manufacturing efficiency.

Cost Implications and Timeline Considerations
Budget Considerations
Cost analysis reveals significant differences between modular and prefab home construction methods. Modular homes typically range from $90-160 per square foot, while prefab homes generally cost between $120-200 per square foot. However, these base figures can vary substantially depending on location, design complexity, and material selection.
For modular homes, the primary cost drivers include factory production (40-50% of total cost), transportation (10-15%), and on-site assembly (20-25%). Additional expenses encompass foundation work (10-12%) and finishing touches (8-10%). The controlled factory environment helps optimize construction costs through reduced material waste and labor efficiency.
Prefab homes present a different cost structure, with components like panels and pre-cut materials accounting for 35-45% of the budget. Site work and assembly costs typically consume 30-35%, while design and engineering fees represent 15-20%. Transportation costs are generally lower than modular homes at 5-8% due to more efficient packaging of components.
Both methods offer potential savings through reduced construction time and minimal weather-related delays. However, factors such as custom design requirements, site accessibility, and local building codes can significantly impact final costs. Industry data indicates that modular construction can achieve 10-20% cost savings compared to traditional building methods, while prefab savings typically range from 5-15%.
Project Timeline Analysis
The construction timeline for modular homes typically ranges from 6-12 weeks for factory production, plus 2-4 weeks for on-site assembly and finishing, resulting in a total project duration of 8-16 weeks. In contrast, prefab homes generally require 12-20 weeks for component manufacturing and 4-8 weeks for on-site construction, totaling 16-28 weeks from start to completion.
Modular construction offers greater schedule predictability due to controlled factory environments, reducing weather-related delays by up to 90%. Factory production continues regardless of site conditions, allowing for parallel processes that significantly compress the overall timeline. Quality control measures implemented during manufacturing also minimize the need for rework, preventing potential schedule overruns.
Prefab homes, while still faster than traditional construction, face more variable timelines due to their component-based approach. The sequential nature of assembly and greater dependence on site conditions can introduce scheduling complexities. However, prefab construction typically achieves 30-50% faster completion times compared to conventional building methods.
Key factors affecting timeline variations include:
– Local permit processing times
– Site preparation requirements
– Transportation logistics
– Workforce availability
– Seasonal considerations
– Complexity of design
– Scope of customization
Project managers should account for these variables when developing construction schedules, particularly in regions with challenging weather conditions or strict regulatory requirements.
Building Codes and Regulatory Compliance
Modular Home Regulations
Modular homes must comply with the International Residential Code (IRC) and local building codes, adhering to the same standards as traditional site-built homes. These structures are subject to rigorous state and federal regulations, including comprehensive inspection processes during manufacturing and assembly phases.
The construction process is overseen by third-party inspection agencies that verify compliance with state-specific modular building codes. Each module receives a certification label, demonstrating adherence to applicable building standards. This certification process includes structural, electrical, plumbing, and mechanical system inspections.
Quality control in modular construction follows a strict protocol, with inspections occurring at multiple stages: during component fabrication, module assembly, and final installation. State-licensed inspectors verify that all materials and construction methods meet or exceed local building requirements.
Additionally, modular homes must satisfy specific transportation regulations, as modules are shipped from factories to construction sites. These requirements include structural reinforcement for transit and precise dimensional limitations to ensure safe transport on public roads.
Foundation requirements mirror those of conventional construction, requiring proper permits and local authority approval. Once installed, modular homes are subject to the same zoning laws, property taxes, and insurance requirements as traditional site-built homes.
Prefab Home Requirements
Prefabricated homes must comply with comprehensive regulatory requirements that ensure safety, quality, and structural integrity throughout the construction process. These homes are subject to both federal and state building codes, with the HUD Code (Housing and Urban Development) serving as the primary federal standard for manufactured housing in the United States.
Local building departments typically require detailed documentation, including architectural drawings, structural calculations, and mechanical systems plans before issuing permits. Third-party inspection agencies, certified by state authorities, conduct regular factory inspections to verify compliance with building codes and quality standards during the manufacturing process.
Engineering requirements for prefab homes include wind load calculations, seismic considerations, and foundation specifications tailored to the installation site. Manufacturers must obtain certification from recognized testing laboratories for materials and assembly methods, while also adhering to energy efficiency standards outlined in the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC).
Transportation and installation of prefab components require specific permits and must follow Department of Transportation regulations regarding size limitations and escort requirements. Additionally, contractors handling on-site assembly must be licensed and certified in prefabricated construction techniques, ensuring proper integration of factory-built components with site-built elements according to local building codes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
When selecting between modular and prefab construction methods for your project, several critical factors must be evaluated to ensure optimal outcomes. The decision should be based on a thorough analysis of project requirements, site conditions, timeline constraints, and budget parameters.
Project scope and complexity play a fundamental role in this decision. While both methods offer efficiency advantages, modular construction typically excels in projects requiring standardized units and repetitive layouts, particularly in commercial modular construction applications. Prefab construction, conversely, may offer greater flexibility for custom designs and unique architectural elements.
Budget considerations extend beyond initial construction costs. Factor in transportation logistics, crane requirements, and on-site assembly expenses. Modular construction often presents cost advantages in labor-intensive markets or remote locations, while prefab might be more economical for projects with unique design requirements or limited transportation access.
Timeline requirements significantly influence the choice between these methods. Modular construction typically offers faster completion times due to parallel factory production and site preparation. However, prefab construction may be more suitable when project phases need to be more flexible or when design modifications are anticipated during construction.
Local building codes and regulations must also be carefully considered. Some jurisdictions have specific requirements for modular construction, while others may be more familiar with traditional prefab methods. Additionally, consider the availability of qualified manufacturers and installers in your region, as this can impact both cost and quality.
Environmental factors and sustainability goals should inform your decision. Both methods can support green building initiatives, but their environmental impact may differ based on transportation distances, material choices, and energy efficiency requirements. Evaluate manufacturers’ sustainability practices and certification capabilities to align with project objectives.
Finally, consider long-term maintenance and adaptability needs. Some modular systems offer easier component replacement or modification, while certain prefab solutions may provide better long-term durability or flexibility for future changes.

